Unlocking the Secrets of Space: How Satellites Work
Introduction:
In our modern world, we rely heavily on satellites for various applications such as communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and scientific research. These incredible machines orbiting high above Earth have revolutionized the way we connect and understand our planet. But have you ever wondered how satellites work? In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating realm of satellite technology, exploring their functionality, orbits, and the crucial role they play in our daily lives.
- What is a Satellite?
At its core, a satellite is an artificial object placed in orbit around a celestial body. In the context of Earth, satellites are launched into space to orbit our planet. They come in various shapes and sizes, from small cubesats to massive geostationary satellites. Satellites are equipped with a range of instruments, antennas, and sensors that enable them to perform specific tasks.
- Types of Satellites:
Satellites can be broadly classified into different types based on their functions and orbits:
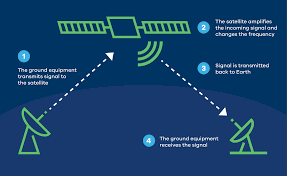
- Communication Satellites: These satellites serve as relay stations, facilitating the transmission of data, voice, and video signals across long distances. They receive signals from ground stations, amplify them, and then transmit them back to other locations on Earth.
- Weather Satellites: Weather forecasting and monitoring satellites observe atmospheric conditions, collect data on temperature, humidity, cloud cover, and provide valuable information to meteorologists, enabling accurate weather predictions.
- Navigation Satellites: Navigation satellites, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), allow precise positioning and timing services. They emit signals that can be received by GPS receivers on the ground, enabling accurate navigation and location determination.
- Earth Observation Satellites: These satellites capture high-resolution images of Earth’s surface, monitoring changes in land use, weather patterns, and natural disasters. They play a vital role in environmental research, urban planning, and disaster management.
- How Do Satellites Stay in Orbit?
Satellites maintain their orbits through a delicate balance between their forward velocity and the gravitational pull of the Earth. When a satellite is launched into space, it is given an initial speed called the escape velocity, which allows it to break free from Earth’s gravity. Once in space, the satellite’s velocity is adjusted to match its desired orbit using small onboard thrusters.
There are several orbit types commonly used by satellites:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Satellites in LEO are relatively close to Earth, ranging from a few hundred kilometers to around 2,000 kilometers in altitude. They orbit the Earth more frequently, providing faster data transmission but with limited coverage.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Satellites in MEO have higher altitudes, typically around 10,000-20,000 kilometers. Navigation satellites like GPS fall into this category, providing global coverage with longer orbital periods.
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO): Satellites in GEO orbit at an altitude of approximately 36,000 kilometers above the equator. They remain fixed relative to Earth’s rotation, allowing them to provide continuous coverage over specific regions.
- Satellite Communication:
Satellite communication involves the transmission of signals between ground-based stations and satellites. When we make a phone call or stream a video, the data is sent to a ground-based station, which relays it to the appropriate satellite. The satellite then amplifies the signal and retransmits it back to Earth, where it is received by another ground station and routed to its destination.
To facilitate communication, satellites use different frequency bands, including radio, microwave, and even optical wavelengths. These signals are carefully transmitted and received using specialized antennas, ensuring efficient data transfer over long distances.
Conclusion:
Satellites have become an integral part of our interconnected world, enabling global communication, precise navigation, weather
monitoring, and much more. By understanding the basics of how satellites work, we can appreciate the technological marvels that make our modern lifestyles possible. From their orbits high above the Earth to the intricate communication systems they employ, satellites continue to shape the way we live, work, and explore our planet.

