Where do Meteoroids Originate within Our Solar System?
Meteoroids, those mysterious objects that streak across our night skies as meteors or, when they survive the journey through Earth’s atmosphere and reach the surface, meteorites, have fascinated humanity for centuries. But where do these enigmatic celestial travelers come from, and what is their origin within our vast solar system? In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll embark on a journey through space to uncover the birthplaces of meteoroids and gain a deeper understanding of these cosmic wanderers.
Defining Meteoroids
Before delving into their origins, let’s define what meteoroids are. Meteoroids are small celestial objects, typically composed of rock, metal, or a combination of both, that range in size from a grain of sand to a few meters in diameter. They are distinct from asteroids, which are larger rocky bodies, and comets, which are icy bodies that develop tails when they approach the Sun. Meteoroids are the precursors of meteors, which are the streaks of light we see when they enter Earth’s atmosphere, and meteorites, which are meteoroids that survive the fiery descent and land on Earth’s surface.
Main Sources of Meteoroids
Meteoroids can originate from various sources within our solar system. Here are the primary contributors:
1. Asteroids: The Rocky Reservoirs
One of the most significant sources of meteoroids is asteroids. These are rocky or metallic bodies that orbit the Sun, primarily within the asteroid belt, a region located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Asteroids are remnants from the early solar system and can range in size from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers in diameter.
Meteoroids can break off from asteroids due to collisions or other forces, becoming independent objects on their own trajectories. These fragments can vary in size and composition, and when they enter Earth’s atmosphere, they produce the meteors we observe as “shooting stars.”
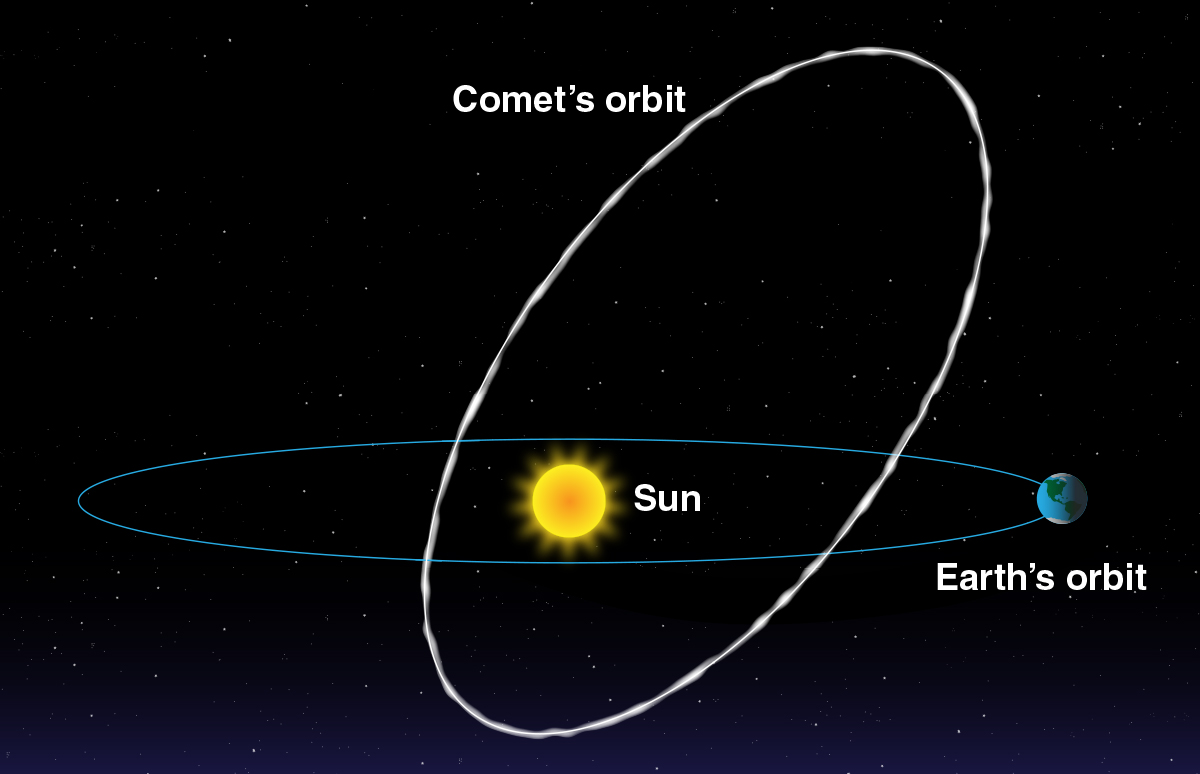
2. Comets: The Icy Contributors
Comets, often referred to as “dirty snowballs,” are another source of meteoroids. Comets are composed of a mixture of water ice, frozen gases, dust, and rocky material. When comets approach the Sun, the heat causes them to release gas and dust, creating the characteristic coma and tails that make them visible from Earth.
Some of the dust and small rocky particles expelled by comets can become meteoroids. When Earth passes through the debris left behind by a comet’s orbit, we experience meteor showers. These showers occur at specific times each year and can be quite spectacular, with hundreds of meteors visible per hour.
3. Moons and Other Planetary Bodies: The Lesser-known Contributors
While less common, some meteoroids can originate from the moons and other planetary bodies within our solar system. These meteoroids are typically fragments from impacts on these celestial objects. For example, the Moon is pockmarked with craters from countless meteoroid impacts, and some of the debris from these impacts can become meteoroids that eventually find their way to Earth.
Interstellar Meteoroids: Cosmic Wanderers
While the above sources primarily contribute meteoroids within our solar system, it’s worth mentioning that there are meteoroids that may come from beyond our solar system. These interstellar meteoroids, often referred to as “extrasolar” or “interstellar” objects, have been of significant interest to astronomers.
The most famous example of an interstellar object is ‘Oumuamua, which passed through our solar system in 2017. Its unusual characteristics and trajectory indicated that it originated from outside the solar system. While rare, the possibility of more interstellar meteoroids passing through our neighborhood of the galaxy adds an extra layer of mystery to the world of meteoroids.
Conclusion
Meteoroids, those transient and captivating travelers of the cosmos, come from a variety of sources within our solar system. They can be remnants from the early solar system, fragments from asteroids or comets, or even debris from impacts on moons and other planetary bodies. The study of meteoroids not only helps us understand their origins but also provides insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. As these celestial nomads continue to journey through space, they remind us of the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the universe.
